OpenShift confidential containers (CoCo) is now generally available for Microsoft Azure. You can extend the security capabilities of Red Hat OpenShift by using OpenShift confidential containers, which allows you to deploy and manage confidential workloads with enhanced data protection and integrity. This release marks a significant milestone, providing a robust solution for enterprises seeking to protect sensitive applications and data on Azure. It addresses critical security concerns by isolating workloads within a hardware-protected trusted execution environment, helping ensure that data remains encrypted even during processing.
Confidential containers on Microsoft Azure solution overview
CoCo integrate trusted execution environment (TEE) infrastructure with the cloud-native world. A TEE is an isolated environment with enhanced security provided by confidential computing-capable hardware, such as Azure cloud infrastructure. A special virtual machine (VM) called a confidential virtual machine (CVM) that executes inside the TEE is the foundation for the OpenShift CoCo solution. CoCo leverages those CVM to create pods inside them which results in a confidential container (pod) for running workloads with enhanced security.
The second part of the CoCo solution is attestation, a process used to verify that the target TEE (where the workload is intended to run) is indeed trusted. The combination of TEE and attestation enables the CoCo solution to provide a trusted environment to run workloads and technically enforce the protection of code and data from unauthorized access by privileged entities. In the CoCo solution, the Trustee project provides the capability of attestation. It’s responsible for performing the attestation operations and delivering secrets after successful attestation.
This diagram shows the overall CoCo solution architecture:
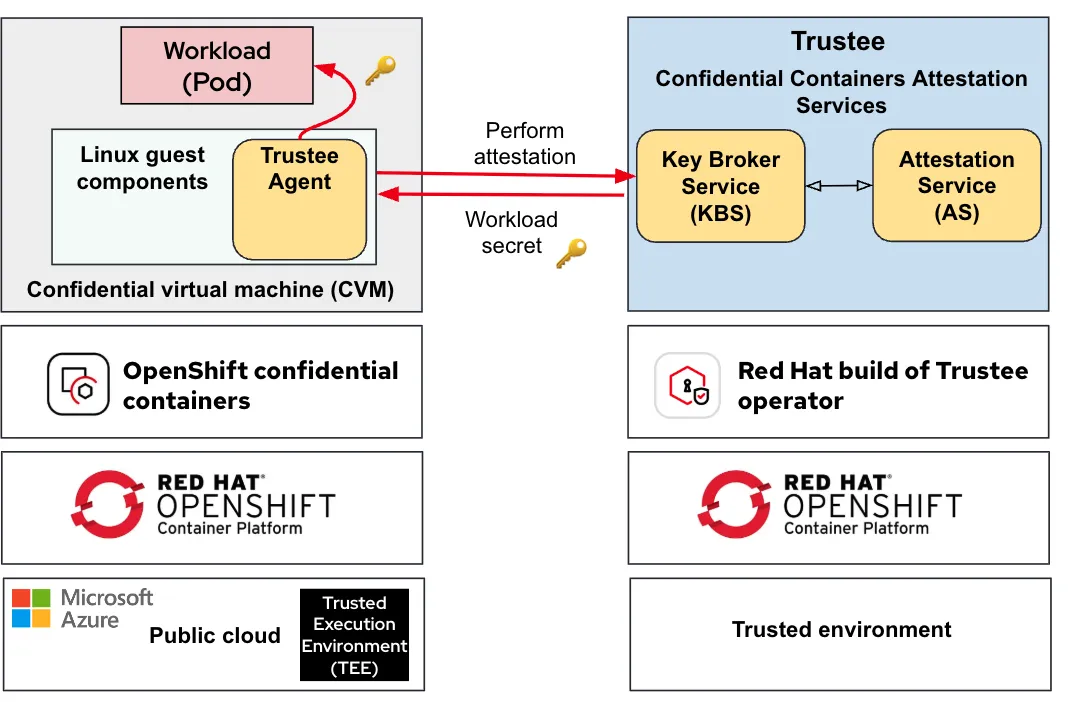
For additional information on the CoCo solution, read Exploring the OpenShift confidential containers solution and Use cases and ecosystem for OpenShift confidential containers.
Integrity protection
Integrity protection is now built into the CoCo pod VM image. It leverages dm-verity, a Linux kernel feature enabling integrity checking for block devices (such as the root disk partition.)
This technology protects the CVM disk from offline attacks: after the CVM Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) disk image is built, no one will be able to inject data into it before it is being used in a CoCo environment, and the root will always remain in a read-only state. Any modification is caught early during startup, causing the system to stop to avoid running in an untrusted state.
In the CoCo workflow, this is extremely important because the CVM disk image is first downloaded into the container platform (untrusted), uploaded into the user cloud-managed image repository (untrusted), and finally deployed in the cloud hardware (untrusted). Disk integrity verification ensures that during this path, no one has tampered with the CVM root file system, therefore protecting the CoCo Linux guest components and the trustee attestation agent stored inside it.
This diagram shows the new integrity protection block protecting the Linux guest components:
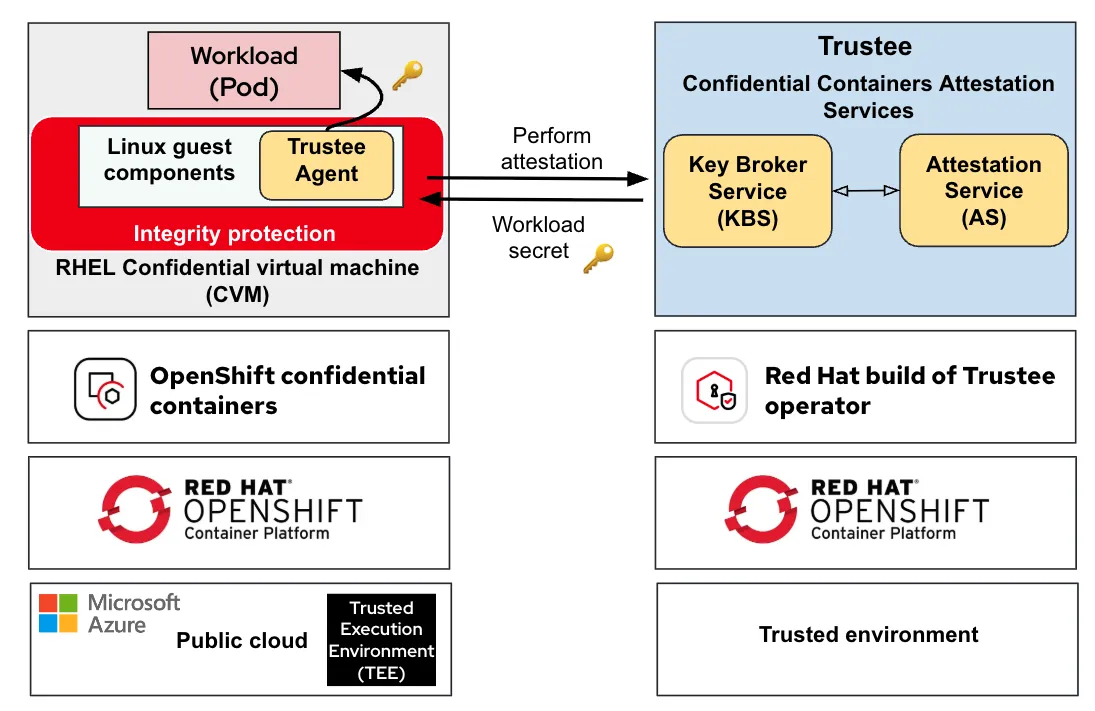
Ensuring that such an integrity mechanism is enabled is part of the standard attestation duties, and it helps prevent a malicious attacker from disabling integrity checks.
Pod bootstrap configuration
CoCo now provides you with the option to add bootstrap configurations through measured initdata.
In previous CoCo releases, multiple configurations at the pod level were static. This includes settings such as defining which Trustee server to use, what operations were allowed in the CoCo pod, what container images could be run in the pod (specific container image digests, for example), and more. Such configurations are now dynamic at the pod through the bootstrap configuration.
Why does this matter?
CoCo pod-level policy configurations, and the support for multiple Trustee servers at the pod level, enable several new use cases including:
- Access control per workload: Configure each pod (workload) with policies governing what commands can be executed and what containers can run in the pod.
- Multi attestation server support: Use multiple Trustee servers and associate each attestation service to specific workloads or tenants.
- Multi tenant trust control: Configure different levels of trust for each tenant or workload by controlling the type of attestation server to use and container level restrictions (for example, only run signed container images).
The following diagram shows how a user injects the bootstrap configuration to a peer-pods CVM before the actual pod (workload) has been created, and before connection with the attestation server has been established:
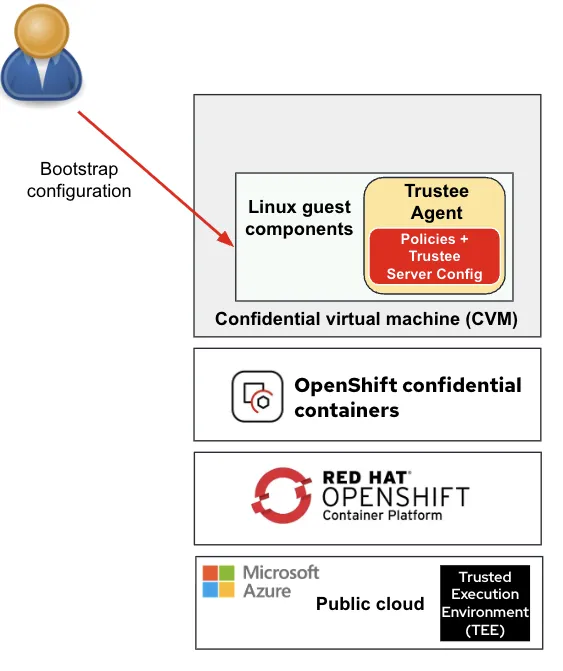
The key block to notice in the above diagram is the policies + trustee server config block (note the Trustee agent, in red) which governs the restrictions on the CoCo pod that's created in the CVM, and also specifies what attestation server this workload can connect to.
Once the bootstrap configuration has been added, the normal flow of creating CoCo workloads and connecting to a Trustee attestation server are initiated:
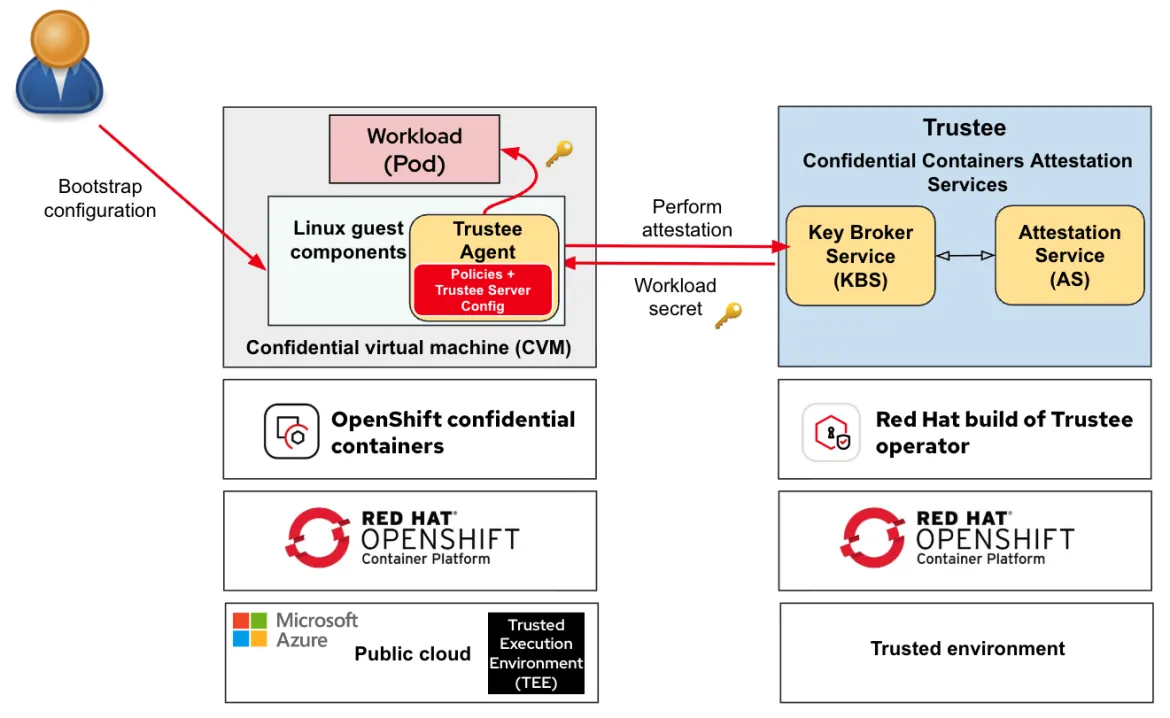
Attestation metrics
The Trustee attestation solution is a key component in the OpenShift confidential containers solution. In this release, Trustee metrics have been added to the solution:
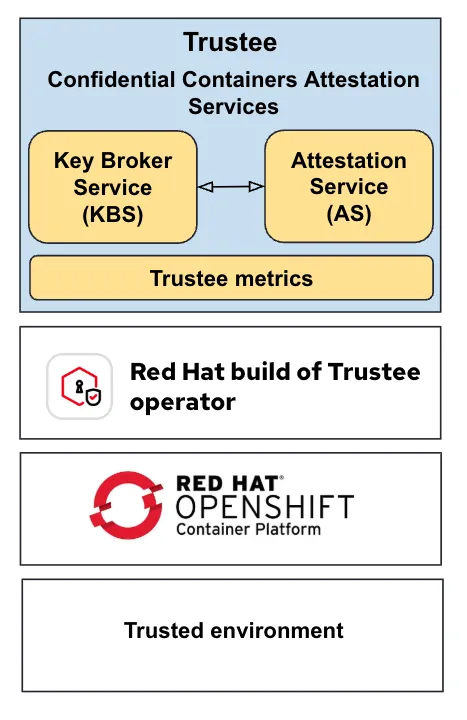
Trustee metrics are based on Prometheus and comprehensive observability to the Key Broker Service (KBS). The metrics include the following:
- HTTP Request Metrics: Total request counts, response times, and request/response size distributions for monitoring KBS API performance
- Resource Access Metrics: Tracking of secret resource reads and writes with per-resource path granularity for auditing and usage analysis
- Metrics Endpoint: Dedicated metrics endpoint for Prometheus scraping with automatic metric registration and cleanup
This enables production monitoring and alerting for KBS deployments, providing visibility into both API performance and resource access patterns critical for confidential container workloads.
Sealed secrets support
A sealed secret is an encapsulated secret available only within a TEE after verifying the integrity of the TEE environment. Sealed secrets allow confidential information to be stored in the untrusted control plane. Similar to other OpenShift secrets, sealed secrets are orchestrated by the control plane and are transparently provisioned to your workload as environment variables or volumes. This diagram shows the flow:
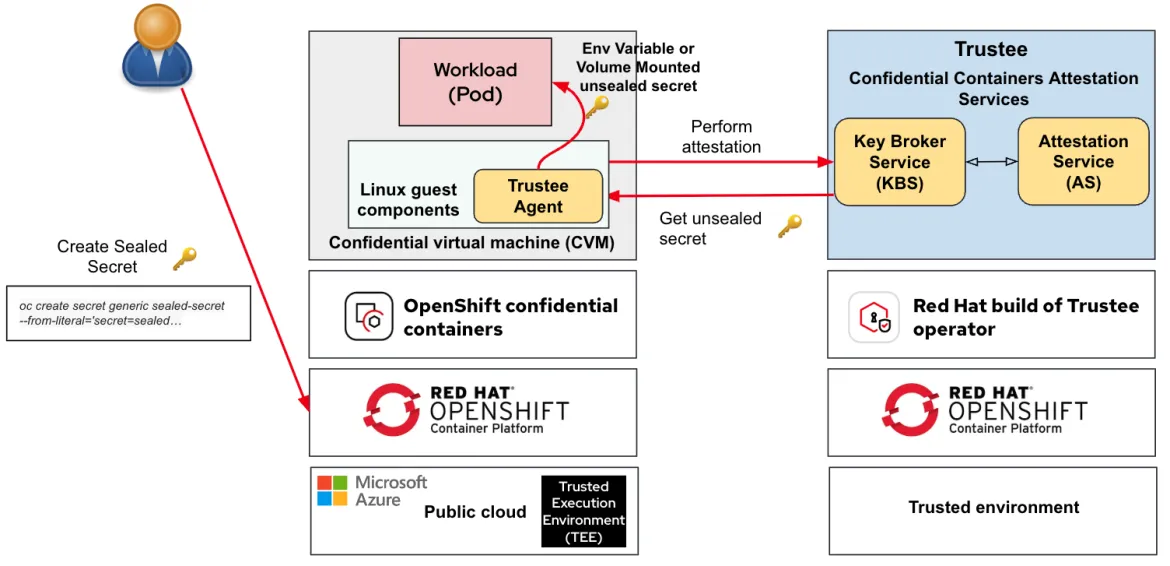
- The user creates the sealed secret, which is a pointer to the actual secret to be retrieved from the Trustee
- The sealed secret is referred to in the pod specification like any regular secret
- Upon successful remote attestation, the Trustee agent retrieves the sealed secret and makes it available through a pod environment variable or volume mount (depending on the pod specification)
For more details on providing secrets to pods, refer to OpenShift documentation.
Secure cloud bursting from on-prem to Azure cloud
Confidential containers secure cloud bursting from an on-prem OpenShift cluster to CoCo workloads running on Microsoft Azure is now supported.
In this use case we have an OpenShift cluster running in an on-prem deployment environment with the OpenShift confidential containers operator installed on it. The Trustee attestation server is deployed on a separate trusted environment. The main difference is that based on different criteria, the OpenShift cluster can decide to security burst a workload to the cloud by spinning up a CoCo workload on Azure. This diagram shows this solution:
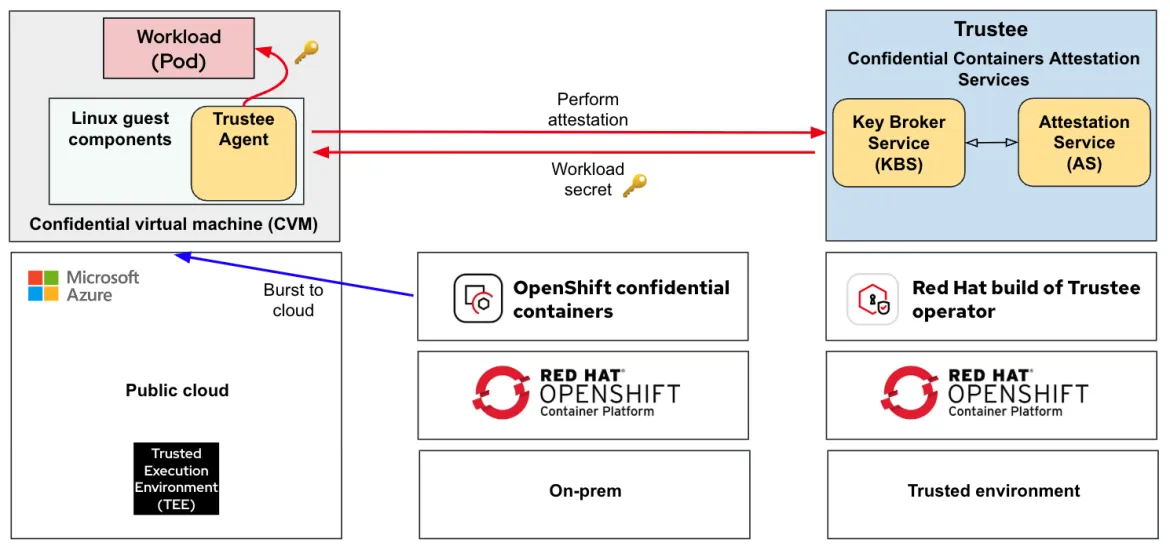
Note the following:
- There is no OpenShift cluster running on Azure. Instead, the cluster is on-prem and we leverage CoCo tools to create the workloads remotely on Azure.
- The look and feel, for a user of the CoCo workloads, is that they are running on the on-prem OpenShift cluster.
- The CoCo workloads perform attestation with the same Trustee attestation server located in a trusted environment (the connection to Trustee must be secured),
- In the future, CoCo workloads will also be supported in on-prem OpenShift deployments. Users can decide whether to create CoCo workloads on-prem or burst out to the public cloud.
For a detailed overview of the CoCo cloud bursting solution, read Secure cloud bursting: Leveraging confidential computing for peace of mind.
Looking to the future
As the OpenShift confidential containers solution continues to evolve, we plan on providing support for additional deployment footprints, including bare metal, additional public clouds, and managed services. Additional key features and capabilities are also expected to roll out such as encrypted container images, confidential GPU support, and more.
Hub
Red Hat Product Security
About the authors
Pradipta is working in the area of confidential containers to enhance the privacy and security of container workloads running in the public cloud. He is one of the project maintainers of the CNCF confidential containers project.
Emanuele Giuseppe Esposito is a Software Engineer at Red Hat, with focus on Confidential Computing, QEMU and KVM. He joined Red Hat in 2021, right after getting a Master Degree in CS at ETH Zürich. Emanuele is passionate about the whole virtualization stack, ranging from Openshift Sandboxed Containers to low-level features in QEMU and KVM.
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds


