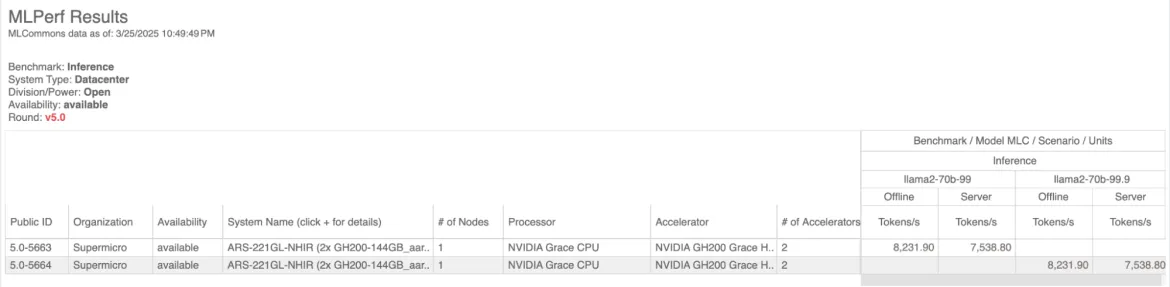
On April 2, 2025, industry-standard MLPerf Inference v5.0 datacenter results were published by MLCommons. Red Hat and Supermicro submitted strong results for the popular llama2 70B model with Red Hat OpenShift running on their dual GPU GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip 144GB server. This was the first time anyone has submitted an MLPerf result with OpenShift on GH200. You can view these results at mlcommons.org.
Llama2-70b
Meta released the Llama2-70b model on July 18, 2023. This model is open source and part of the very popular Llama family of models that range from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters. In this round of MLPerf Inference Datacenter there were 17 organizations who submitted Llama 2 70B results, making it the most popular model in this round.
The Supermicro MLPerf v5.0 dual GPU GH200 server submission ran OpenShift 4.15 and NVIDIA TRT-LLM for the server stack. TRT-LLM uses post-training quantization to quantize llama2-70b to FP8 precision (8-bit floating point). FP8 dramatically reduces the memory footprint and bandwidth requirements allowing larger batch sizes and longer sequences. FP8 quantization also allows faster computation, but is less precise. This quantized model was used in the Supermicro MLPerf v5.0 submission and takes advantage of the FP8 hardware in GH200 systems.
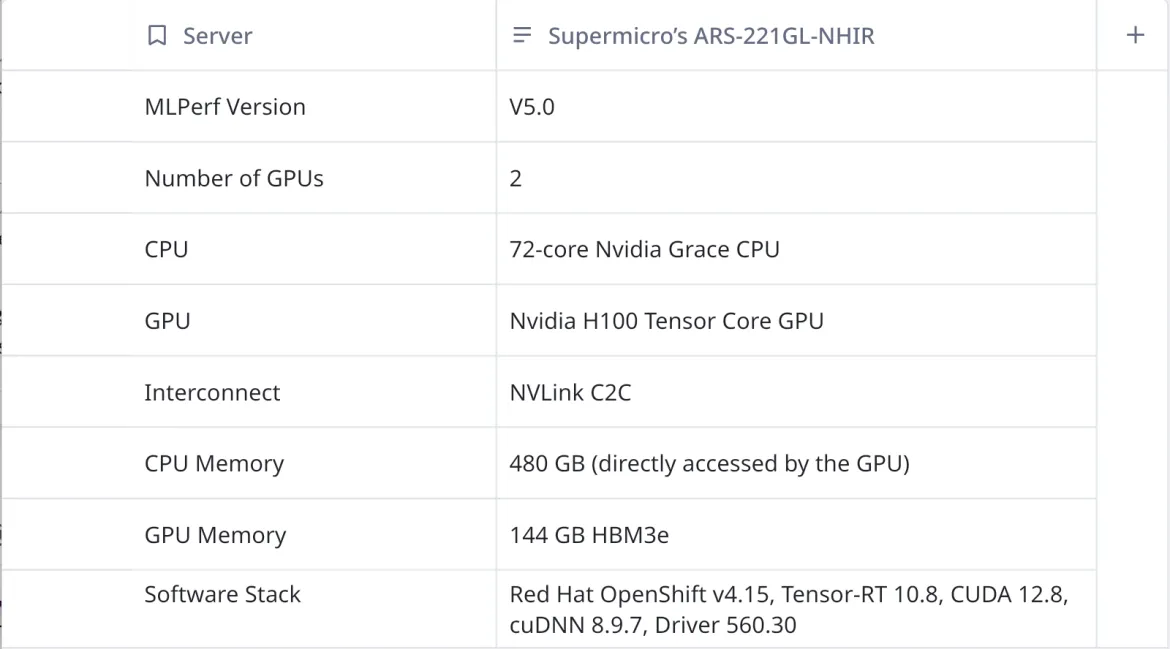
In this submission, OpenShift 4.15 and TRT-LLM were used together and the system under test was is shown here:
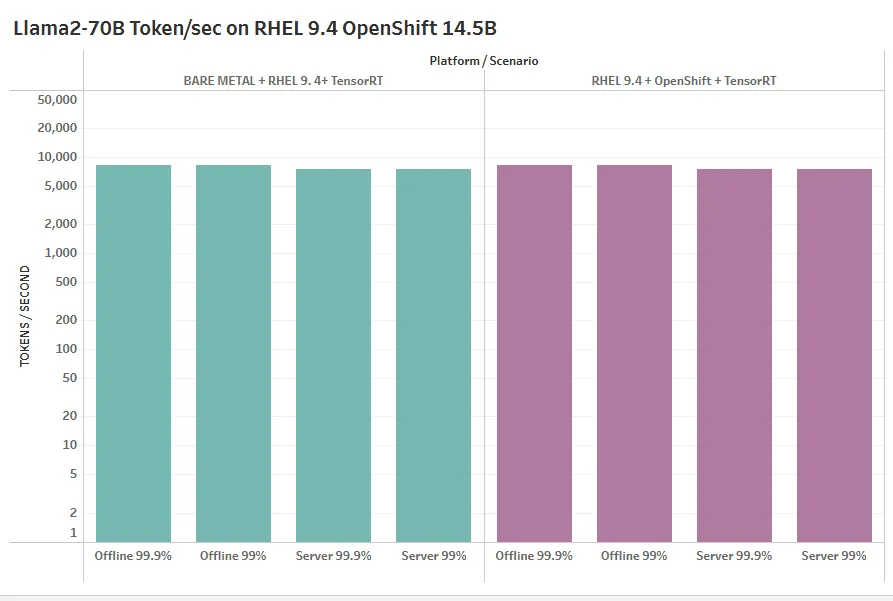
In addition to the excellent results submitted for MLPerf Inference v5.0 we were able to demonstrate on the Supermicro GH200 dual GPU system that OpenShift results were comparable to bare metal Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9.4 results. The chart below shows that OpenShift added less than 2% overhead in these four scenarios for Llama2-70b.
System details
ARS-111GL-NHR ( 144 GB GPU)


Key applications
- High Performance Computing
- AI/Deep Learning Training and Inference
- Large Language Model(LLM) and Generative AI
Key features
This system currently supports two E1.S drives direct to the processor and the onboard GPU only. Please consult your Supermicro salesperson for details.
- High density 1U GPU system with Integrated NVIDIA® H100 GPUa
- NVIDIA Grace Hopper™ Superchip (Grace CPU and H100 GPU)
- NVLink® Chip-2-Chip (C2C) high-bandwidth, low-latency interconnect between CPU and GPU at 900GB/s
- Up to 576GB of coherent memory per node including 480GB LPDDR5X and 96GB of HBM3 for LLM applications.
- 2x PCIe 5.0 X16 slots supporting NVIDIA BlueField®-3 or ConnectX®-7
- 9 hot-swap heavy duty fans with optimal fan speed control
- This system supports two E1.S drives directly from the processor only
Easy to use
It is easy to run the MLPerf benchmarks with OpenShift. Operators can be selected and installed from the Operator hub. These operators automate the management of everything from storage to the NVIDIA accelerated compute resources.
The OpenShift Storage Operator makes it easier to automate the process of running multiple benchmarks. It allows you to create what is essentially a repository for models and then easily switch between them in your pod manifest. We were able to load multiple models into storage and easily switch between them. The Storage Operator automatically provisioned storage for these models when persistent volume claims (PVCs) were created.
The NVIDIA GPU Operator makes it easier to install required NVIDIA drivers, container runtimes and other libraries used to access the NVIDIA GPUs on OpenShift.
Conclusion
Supermicro and Red Hat have demonstrated competitive performance for the MLPerf Inference v5.0 benchmarks with Llama-2-70b. The results were essentially the same on RHEL 9.4 and OpenShift 4.15 showing that OpenShift adds both usability and monitoring capabilities without sacrificing performance.
resource
Get started with AI for enterprise: A beginner’s guide
About the authors
Diane Feddema is a Principal Software Engineer at Red Hat Inc in the Performance and Scale Team with a focus on AI/ML applications. She has submitted official results in multiple rounds of MLCommons MLPerf Inference and Training, dating back to the initial MLPerf rounds. Diane Leads performance analysis and visualization for MLPerf benchmark submissions and collaborates with Red Hat Hardware Partners in creating joint MLPerf benchmark submissions.
Diane has a BS and MS in Computer Science and is presently co-chair of the Best Practices group of the MLPerf consortium.
Nikola Nikolov is AI/HPC solutions engineer from Supermicro. Nikola received PhD in Nuclear Physics from the University of Knoxville, Tennessee focused on large-scale HPC computations in Nuclear Astrophysics at Oak Ridge National Laboratory under National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) Stewardship grant.
Before joining the industry, he spent last years in academics designing experiments with CERN Isolde collaboration and Cosmic Neutrino Detection with Los Alamos National Laboratory.
Prior to Supermicro, Nikola worked at KLA+ Inc. (former KLA-Tencor) as Big Data and ML developer in semiconductor industry. He designed HBase, Big-Table, and Data Lake infrastructures for Anomaly Detection and Failure Predictive analysis of semiconductor equipment. These Big-Data systems have been implemented successfully by major chip manufacturing companies like TSMC, Samsung, and SK Hynix.
Nikola has published both Peer-Reviewed academic articles in top scientific journals like Physical Review Letters and Nature, as well as engineering papers in Big Data management.
In the last 8 years he have focused mainly on public and hybrid cloud solutions with AWS and Google Cloud Platform. In Supermciro, Nikola works mostly into designing cutting edge AI/HPC infrastructure solutions as well as validating AI/HPC systems via MLPerf and HPC benchmarking.
Arpitha Srinivas is an AI Systems Performance Engineer at Supermicro, specializing in optimizing large-scale AI models such as Llama 4, Llama 3.1, Llama 2-70B, BERT, Stable Diffusion, ResNet, and 3D-Unet across NVIDIA (B300, B200, H200, GH200, H100), AMD (MI350, MI325X, MI300X), and Intel (Xeon) platforms. With a master’s degree in AI Software Engineering from San José State University, she brings deep expertise in TensorRT, vLLM, CUDA, ROCm, and MLPerf benchmarking. She has successfully submitted multiple rounds of MLCommons MLPerf Inference and Training benchmarks. Her research paper, "Cyber-Security Dashboard: An Extensible Intrusion Detection System for Distributed Control Systems," was accepted at the IEEE SVCC 2025 Conference. Arpitha is a passionate advocate for women in technology and has contributed to several industry conferences. She also reviews for O’Reilly Media books. When not tuning AI systems and models she enjoys hiking, music, and painting.
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds

