Red Hat OpenShift 4.19 is now generally available. Based on Kubernetes 1.32 and CRI-O 1.32, OpenShift 4.19 enables robust AI workloads, provides flexibility for virtualization and security, and continues to support Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus. OpenShift provides a trusted, comprehensive and consistent application platform enabling enterprises to innovate faster across the hybrid cloud, without compromising on security.
Available in self-managed or fully managed cloud service editions, OpenShift offers a complete set of integrated tools and services for cloud-native, AI, virtual and traditional workloads alike. This article highlights the latest OpenShift 4.19 innovations and key enhancements. For a comprehensive list of updates and improvements, refer to the official release notes.
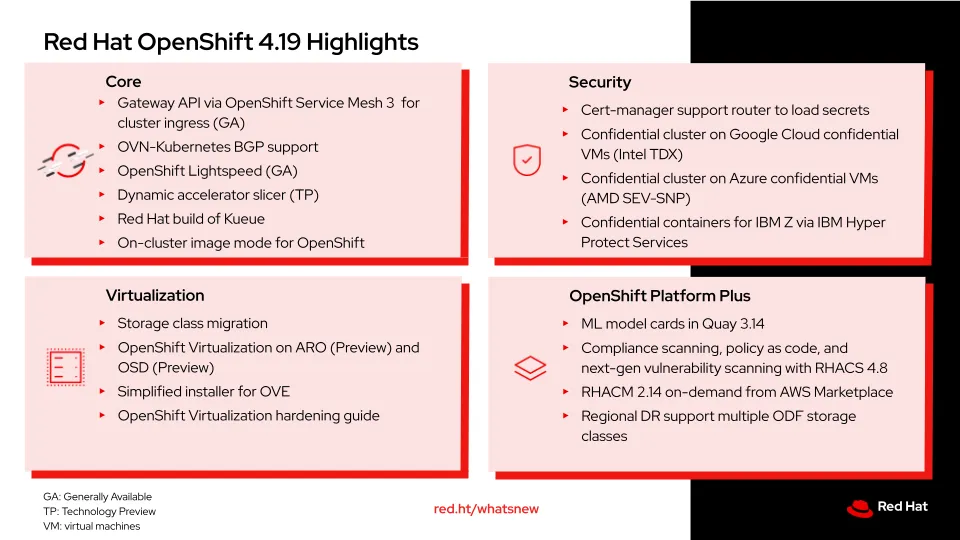
Red Hat OpenShift 4.19 highlights
Modernize ingress with Gateway API with OpenShift Service Mesh 3 for unified and extensible ingress
This release marks the general availability of Gateway API with OpenShift Service Mesh 3 in OpenShift 4.19. As the emerging gold standard for ingress in Kubernetes, Gateway API offers a flexible and role-oriented model for controlling how external traffic reaches services within your cluster. It acts as a powerful traffic controller, enabling L4/L7 traffic routing, dynamic load balancing, and TLS termination through standard custom resource definitions.
OpenShift, which already supported Routes and Ingress, extends that out-of-the-box support to include Gateway API backed by Istio. Importantly, you don't need Service Mesh to use Gateway API—but when you do, the OpenShift Ingress Operator handles the full lifecycle: installing Istio via OpenShift Service Mesh, managing DNS and load balancer configurations, and deploying an Envoy-based gateway. For users of third-party Gateway API implementations, DNS and LB management must be handled manually. Gateway API offers greater flexibility and expressiveness than the legacy Ingress API, enabling precise control over complex traffic flows while delivering scalable, observable ingress management tailored for modern cloud-native workloads.
Seamless integration between OpenShift Networking and customer external networks with BGP
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a routing protocol used to advertise route information with other BGP peers. It's supported in an early z-stream release of OpenShift 4.19. Limited BGP support already exists today in MetalLB to advertise load balancer Kubernetes service IPs. OpenShift 4.19 extends BGP support into the core of OpenShift Networking so you can import and advertise routes of pod and virtual machine (VM) networks to BGP peers outside the cluster, integrating directly with the provider's networking fabric. In combination with VRF-Lite support, you can extend a provider VPN into an OpenShift cluster for VMs and pods, defined as a User Defined Network (UDN). You can also advertise egress IP addresses with BGP.
OpenShift Networking BGP support includes support for bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD), a protocol that enables fast detection of link failures in network devices. This can quickly identify when a link or a path between devices is down, and allow them to adjust routing and forwarding information.
Accelerate Red Hat OpenShift expertise with Red Hat OpenShift LightSpeed
This new release includes OpenShift Lightspeed, a generative AI virtual assistant integrated directly into the OpenShift platform. With OpenShift Lightspeed, novice users can acquire platform skills quickly, and experienced users can scale their expertise for production operations. Key features include natural language troubleshooting assistance, flexible integration with multiple AI model providers including OpenAI, Azure OpenAI and IBM WatsonX, as well as technology preview capabilities for cluster interaction and Bring Your Own Knowledge integration. The solution also extends intelligent assistance to OpenShift Virtualization, simplifying VM migrations and modernization efforts by providing readily accessible answers to virtualization-specific questions. Curious to see it for yourself? Check out the demo showcasing OpenShift Lightspeed in action.
Optimize AI workloads with dynamic GPU slicing
We're focused on ensuring OpenShift and Red Hat OpenShift AI together continue to deliver innovative solutions to help you accelerate your AI journey, including a full end-to-end machine learning operations (MLOps) lifecycle with model development, training, tuning, generative AI, and other AI workloads across private data centers, cloud and edge environments. Two new exciting AI-related features in this release include dynamic accelerator slicer and the Red Hat build of Kueue.
Dynamic accelerator slicer, available as a technology preview, dynamically allocates GPU slices on-demand, based on workload requirements, thus optimizing GPU utilization and reducing costs. Dynamic accelerator slicer replaces static pre-slicing resource allocation, which results in under utilized GPU when the workload demands don’t match the preconfigured GPU partition size. The primary use for dynamic accelerator slicer includes running multiple LLM inference instances, such as Red Hat AI Inference Server on a single GPU to support multi-tenant environments where teams share GPU resources to enable cost-effective AI development, testing, and serving workflows.
Streamline AI operations using intelligent job queueing
The Red Hat build of Kueue is a centralized Kubernetes-native job queueing system that manages batch workloads by intelligently scheduling, prioritizing and allocating cluster resources based on quotas and availability. The system addresses resource contention by queuing jobs until sufficient compute, memory, or GPU resources become available, then automatically releasing them back to the pool upon completion. Primary uses of the Red Hat build of Kueue include managing machine learning training pipelines, high-performance computing workloads, and batch processing jobs in multi-tenant environments where teams need fair resource sharing and priority-based scheduling. Learn more about Kueue and other open source technologies in the special O’Reilly report on Scalable Kubernetes infrastructure for AI Platforms.
Both the dynamic accelerator slicer and the Red Hat build of Kueue can be used with AI platforms like OpenShift AI. Red Hat OpenShift AI provides an AI platform, built on OpenShift, for managing the lifecycle of predictive and generative AI models at scale across hybrid cloud environments.
Customize Red Hat OpenShift nodes to accelerate agent and driver deployment
OpenShift's on-cluster image mode gives enterprises more control over OpenShift cluster nodes. It provides a self-contained solution for the creation and management of customized operating systems images within a cluster, wherein Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) is treated like a container image that can be managed as code, built as a unified image, and deployed consistently across entire OpenShift fleets. This capability enables organizations to add non-containerized agents, specialized hardware acceleration drivers, or monitoring tools directly to RHCOS while maintaining customizations through cluster updates. Now, customers don’t have to wait for the next OpenShift release to deploy custom content updates. More significantly, the entire build process occurs directly on the cluster itself, eliminating the need for external CI/CD pipelines and streamlining operations for platform teams managing large-scale deployments.
Create routes with externally managed certificates
In OpenShift 4.19, routes can now be configured to consume TLS certificates from third party certificate management solutions by utilizing the .spec.tls.externalCertificate field in the route API. This allows the route to reference TLS certificates through Secrets resources, thereby taking advantage of the power of the cert-manager operator for Red Hat OpenShift to automatically manage, renew, and rotate certificates at scale.
Better secure data in use with confidential computing across Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud
Security is paramount to everything we do, and we continue to incorporate security capabilities throughout the platform and application lifecycle including expanding our confidential computing solutions in OpenShift. OpenShift adds support for confidential clusters across major cloud providers to help protect data in use through hardware-based cryptographic isolation, helping data remain protected not just at rest and in transit, but during active processing, addressing compliance requirements for regulated industries and multi-tenant environments where traditional security boundaries are insufficient.
On Google Cloud, OpenShift expands its support of Confidential Nodes deployments on confidential VMs to include VMs powered by Intel TDX and AMD SEV-SNP. OpenShift on Confidential Nodes allow users to better secure data in use with hardware-based cryptographic isolation — even from the cloud provider itself — without requiring changes to application code. Similarly, OpenShift 4.19 can be deployed on Azure confidential VMs powered by AMD SEV-SNP VMs, which offers robust hardware-enforced boundaries that help protect workloads from hypervisor-level threats and ensure compliance for regulated industries. In addition, IBM is integrating confidential containers in OpenShift for IBM Z via Hyper Protect Services, leveraging OpenShift Sandboxed Containers to isolate containers from both infrastructure and Kubernetes administrators.
Expand OpenShift Virtualization across all major clouds with simplified migration
On the virtualization front, customers can now migrate VMs from one storage class to a different storage class within a single cluster, making it easier to perform bulk VM migrations. To see this feature in action, check out the Storage Live Migration for OpenShift Virtualization. Customers can also now run Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization virtually anywhere, including AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, on-premises on bare metal. OpenShift Virtualization is already available in Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS, and it’s also now available as a preview on Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift and also a preview on Red Hat OpenShift Dedicated. OpenShift 4.19 makes it easier for novice users to onboard to OpenShift Virtualization with a simplified OpenShift Virtualization installer experience that deploys OpenShift, OpenShift Virtualization, and all the necessary operators without the customer having to touch a single YAML or CLI.
Manage your fleet at scale with Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus
Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus brings solutions that help enterprises with advanced security features available at build, deploy, and runtime. OpenShift Platform Plus helps customers to manage, and automate intelligent applications at scale. Notable highlights include the upcoming Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes 4.8 compliance scanning, policy as code, external IPs reach general availability. Furthermore, the next generation vulnerability scanner using Vex data feed and includes language scanning capabilities becomes the default. Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes is now available on-demand in the AWS Marketplace, providing on-demand pricing and a simplified, consolidated billing option for customers who run Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS. Data protection and disaster recovery continues to be a top focus for Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation, and a top feature in the release is regional Disaster Recovery support for multiple ODF storage classes.
Try Red Hat OpenShift 4.19 today
Get started today with the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console and take advantage of the latest features and enhancements in OpenShift. To find out what’s next, check out the following resources:
- What’s New and What’s Next in Red Hat OpenShift
- What’s New in Red Hat OpenShift 4.19
- In the Clouds (coming on 26 June 2025)
- OpenShift YouTube Channel
- OpenShift Blogs
- OpenShift Commons
- Red Hat Developer Blogs
- Red Hat Portfolio Architecture Center
- Validated Patterns
A complete list of the Red Hat OpenShift 4.19 updates are in the OpenShift 4.19 Release Notes. Send us feedback through your Red Hat contacts or create an issue on GitHub.
product trial
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform | Product Trial
About the author
Ju Lim works on the core Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform for hybrid and multi-cloud environments to enable customers to run Red Hat OpenShift anywhere. Ju leads the product management teams responsible for installation, updates, provider integration, and cloud infrastructure.
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
